A good helper for cold chain logistics: smart RFID tags
Imagine a box of freshly picked strawberries or important vaccines, transported from the factory to the supermarket or hospital, and kept in a frozen or refrigerated environment. If the temperature is high, it will spoil. So how do we know if the temperature has changed along the way? At this time, RFID tags come in handy!

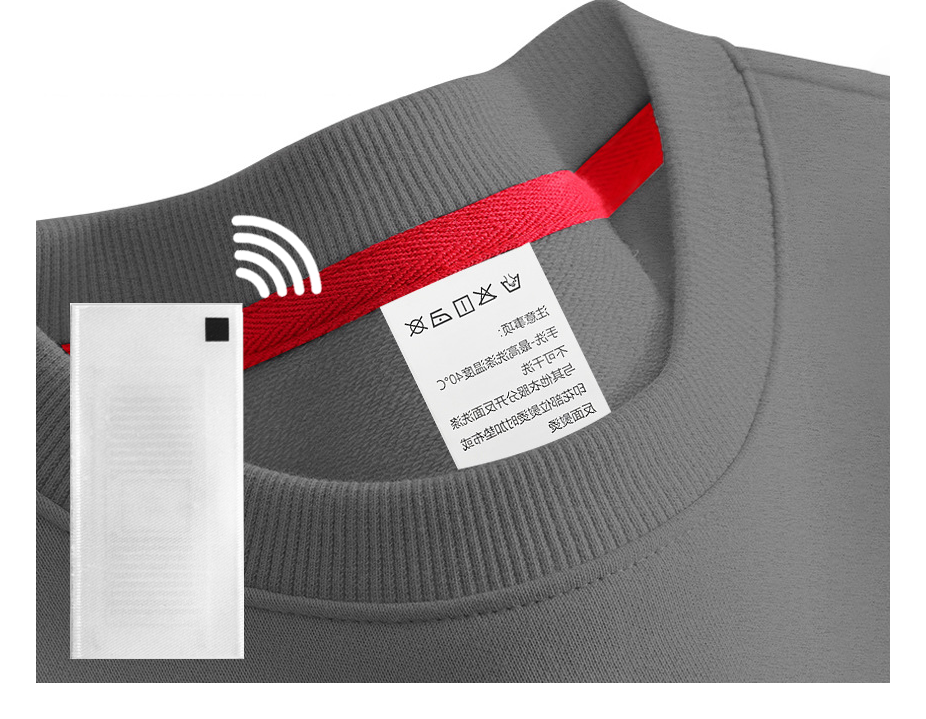
In cold chain logistics (the process of transporting frozen or refrigerated things), RFID can help us do many things:
1. Keep things from spoiling and make the quality safer
We use RFID tags with temperature sensors to monitor the temperature of the goods in real time.
If the temperature is wrong, such as getting hot, it will immediately sound an alarm to remind the staff to deal with it quickly to avoid spoilage.
This is especially important for fresh vegetables, fruits, milk, vaccines, and medicines.
2. Faster transportation and easier work
RFID can read many tags at the same time, unlike barcode scanners that have to read them one by one, so loading and unloading can be completed faster.
RFID systems can also be connected to warehouse or transportation software to automatically update inventory and arrange routes, saving time and manpower.
3. The entire transportation process is clear
Each RFID tag will record important information such as temperature changes, transportation time, and location.
Whether it is a production factory, logistics company, or store, it can track where the goods are and what their status is in real time.
All information can be placed on a platform for everyone to check at any time, which is convenient and transparent.
4. Save money and worry
With the temperature monitoring function of RFID, the number of goods scrapped due to deterioration can be greatly reduced, especially those expensive medicines or imported fruits.
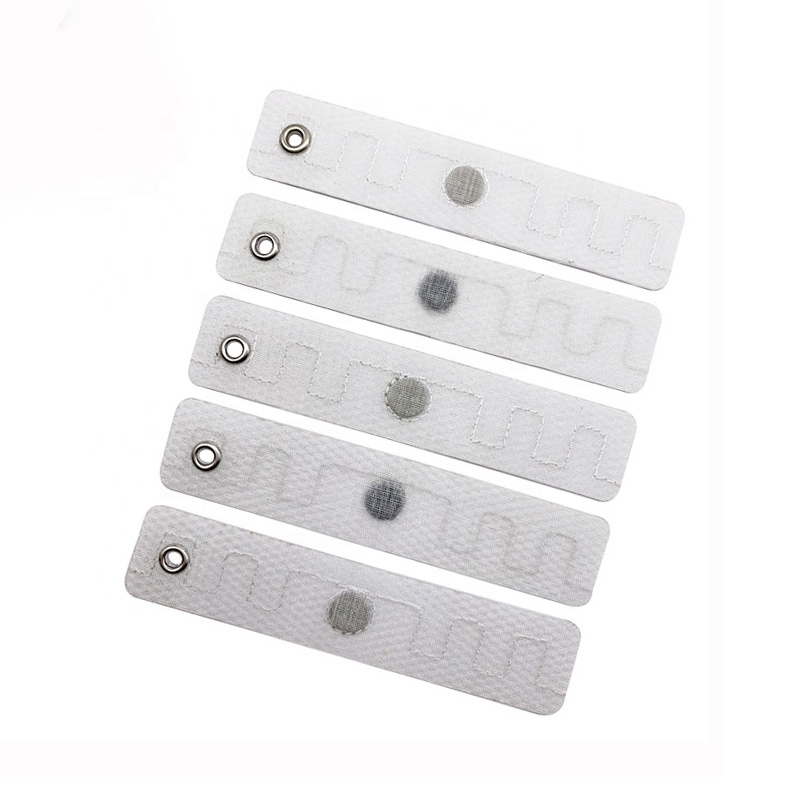
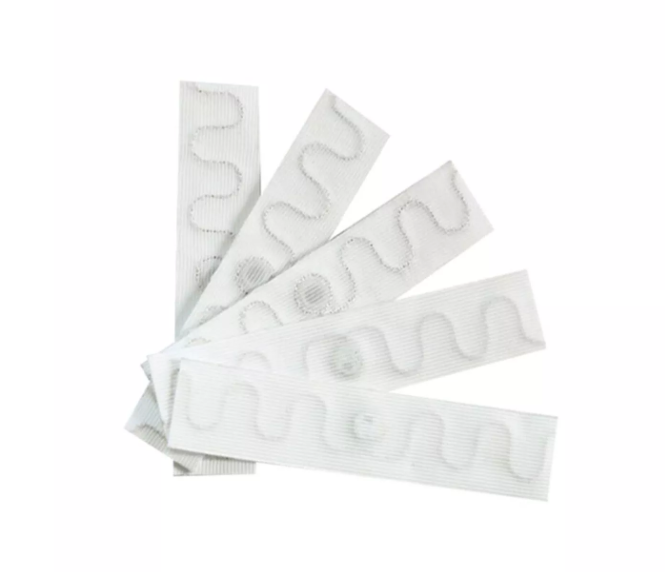
What’s special about our RFID tags?
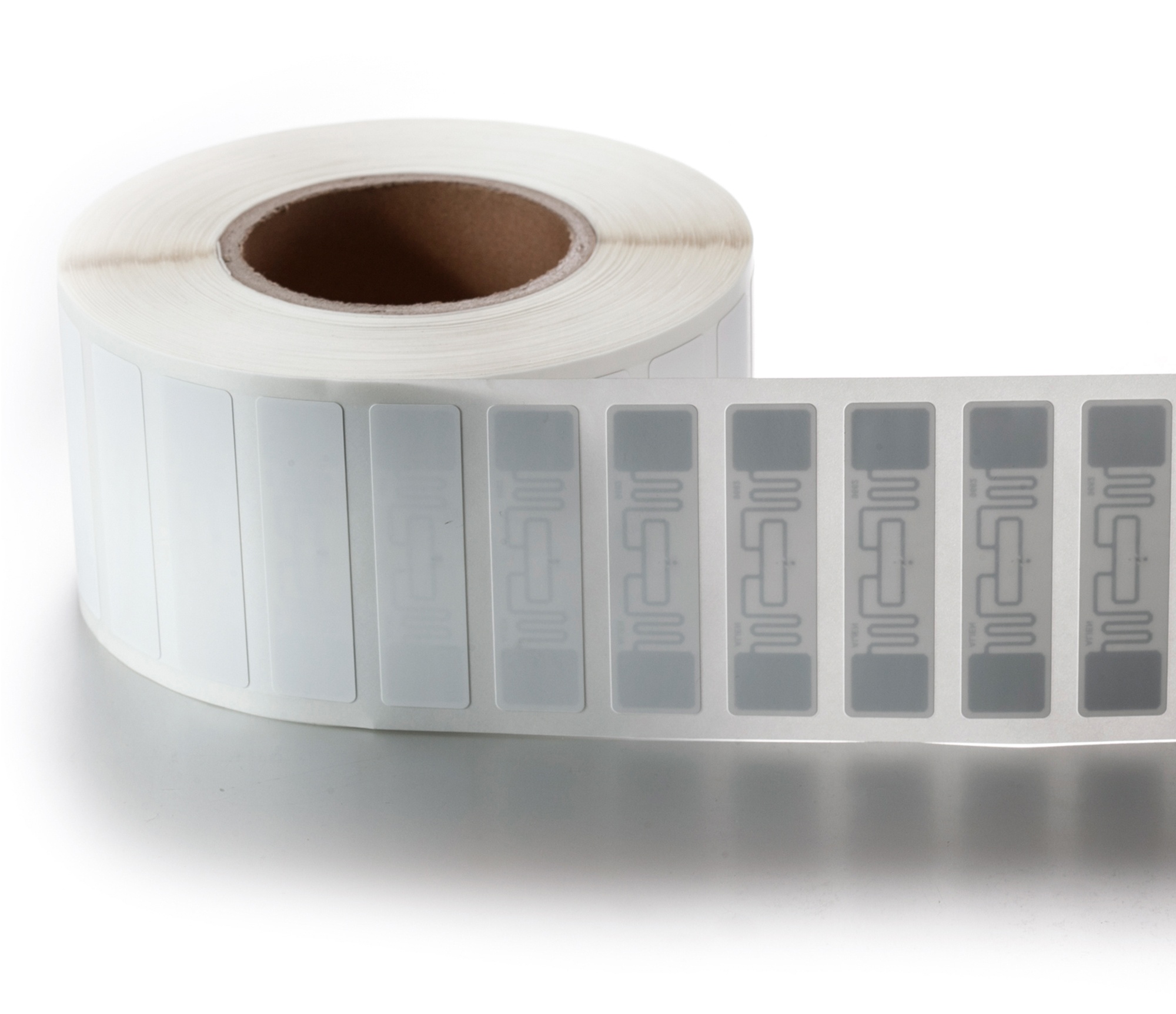
In order to adapt to the temperature-sensitive environment of the cold chain, we have specially designed powerful RFID tags:
Functional Features Description
Chip type Alien H9 or Ucode8/9 are optional, suitable for different needs
Working frequency 860-960 MHz, support UHF high frequency band, stable transmission
Communication protocol ISO/IEC 18000-6C (international standard)
Tag size 100×33mm (other sizes can also be customized)
Material options Coated paper, PVC, PET, waterproof and pressure-proof
Protection ability Water-resistant, heat-resistant, and weather-resistant, no matter how far the transportation is, it is not afraid
Reading distance Can be read at a long distance, suitable for large warehouses and trucks